What is a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve and How Does It Work
A pneumatic solenoid valve is a crucial component in modern pneumatic systems, acting as an electromechanical device that controls the flow of air or gas. It operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, which in turn opens or closes the valve. This swift and reliable operation is essential in various applications, from automated assembly lines to HVAC systems, where precise control of air pressure and flow is required. Understanding how a pneumatic solenoid valve works is vital for engineers and technicians alike, as it not only enhances system efficiency but also ensures safety and reliability in operations.
In this article, we will delve into the inner workings of a pneumatic solenoid valve, exploring its design, functionality, and the benefits it brings to industrial processes. We will examine the principles of solenoid operation, including the electromagnetic forces that drive the mechanism, and the different types of pneumatic solenoid valves available in the market. By the end, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how these valves contribute to the effective management of pneumatic systems, highlighting their pivotal role in automation and fluid control.
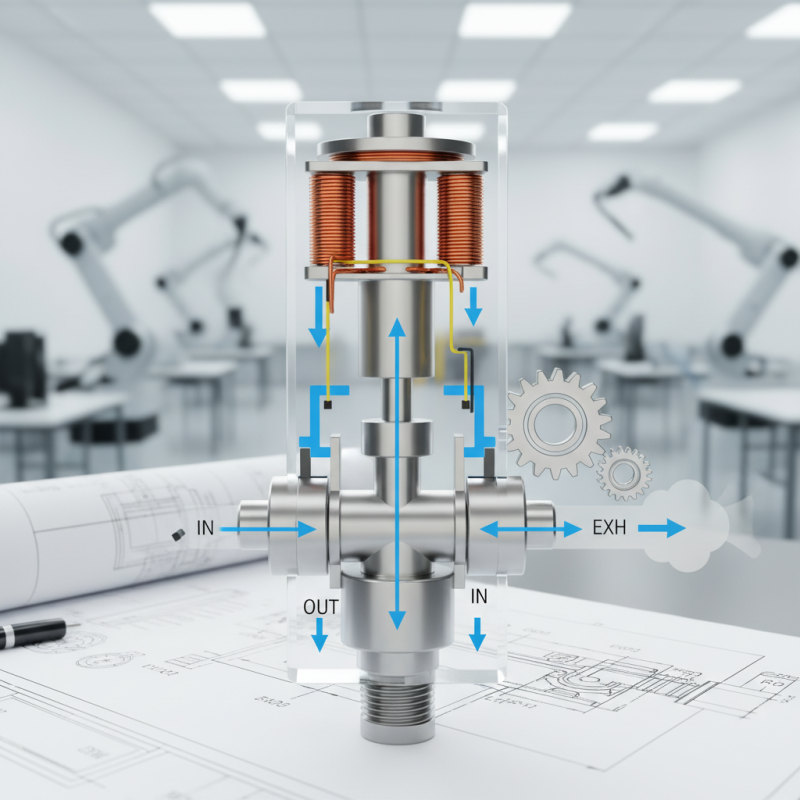
What is a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve?
A pneumatic solenoid valve
is a type of electromechanical valve that operates using compressed air to control the flow of gases or liquids in various applications. These valves typically consist of a solenoid, which is an electromagnetic coil that, when energized, creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger or armature.
This movement either allows or blocks the flow through the valve, enabling precise control of pressure and volume in pneumatic systems. The advantages of pneumatic solenoid valves include fast response times and the ability to handle a wide range of pressures, making them ideal for applications in industries such as manufacturing and automation.
The demand for pneumatic solenoid valves is reflected in the growing flow control valve market, which includes various types of control valves. By 2035, the market is expected to expand significantly, driven by the increasing need for efficient flow management in sectors like oil and petrochemicals, power generation, and food processing. Innovations in valve technology, such as advancements in precision injection systems, highlight a trend toward more specialized and efficient applications of pneumatic controls. This sector's growth demonstrates the significance of pneumatic solenoid valves in optimizing production processes and maintaining operational integrity across diverse industries.
The Basic Components of a Pneumatic Solenoid Valve
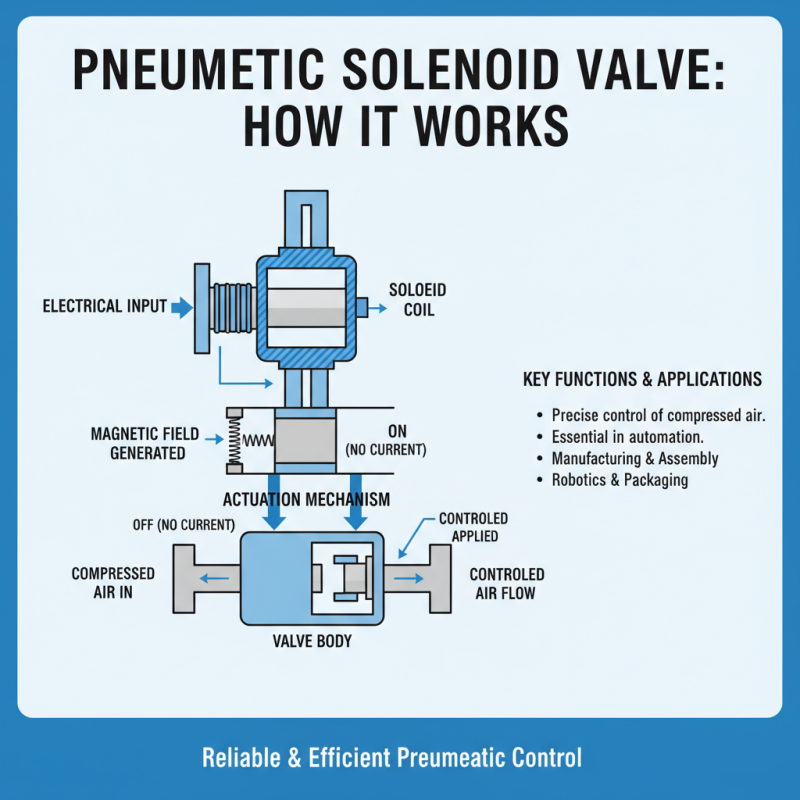
Pneumatic solenoid valves are essential components in various automation and control systems. These valves primarily consist of a solenoid coil, a valve body, and a mechanism that opens or closes the valve based on electrical signals. When electrical current passes through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that actuates the internal mechanism, allowing or blocking the flow of compressed air. This functionality is vital in systems requiring precise control over pneumatics, such as in manufacturing and assembly processes.
The basic components of a pneumatic solenoid valve ensure reliability and efficiency in operation. The valve body is typically made of durable materials that can withstand the pressures and stresses of pneumatic systems. Additionally, the actuator mechanism must be designed for quick response and minimal leakage, as efficiency is critical in pneumatic applications. The integration of these components contributes to the overall performance of pneumatic systems, facilitating advancements and innovations in diverse industries, reflected in the growing market projections for pneumatic components and valves.
How Pneumatic Solenoid Valves Function: A Step-by-Step Process
Pneumatic solenoid valves play a crucial role in various automation systems, acting as electronic switches that control the flow of air in pneumatic circuits. The mechanism of operation begins with an electrical signal sent to the solenoid, which energizes the coil. According to a report from the International Society of Automation, approximately 45% of industrial automation systems utilize solenoid valves for their reliability and efficiency in controlling fluid dynamics.
Once the solenoid is energized, it creates a magnetic field that pulls a plunger or armature within the valve. This movement either opens or closes ports within the valve body, allowing compressed air to flow through or stop fluid movement altogether. Industry statistics highlight that pneumatic systems can operate at pressures ranging from 30 to 130 psi, making solenoid valves essential for maintaining precise control over these pressures in various applications, such as in automotive assembly lines and packaging machinery.
As the valve returns to its default position when the electrical signal is removed, the system can automatically restore the airflow path. This cycle of activation and deactivation enables effective control of machine functions, validating the importance of pneumatic solenoid valves in enhancing operational efficiency and safety in automated processes.
Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Performance Metrics
This chart illustrates key performance metrics of a pneumatic solenoid valve, including opening and closing times, operating pressure, and flow rate. These parameters are crucial for understanding how a solenoid valve functions within a pneumatic system.
Applications of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves in Industry

Pneumatic solenoid valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications, particularly in automation and fluid control systems. Given the projected growth in the global pneumatic components market—expected to increase from $14.81 billion in 2025 to $21.58 billion by 2032—these valves are becoming more integral in manufacturing processes. Industries are increasingly adopting pneumatic solenoid valves for their ability to provide precise control over pneumatic systems, leading to improved efficiency and reliability in operations.
The solenoid valve market, in particular, is anticipated to experience significant growth, with a projected value rising from USD 4.9 billion in 2025 to USD 7.6 billion by 2035, reflecting a CAGR of 4.5%. Applications in sectors such as packaging, automotive, and electronics leverage the benefits of solenoid valves, including their quick response times and low energy consumption. As businesses seek to enhance productivity, the demand for pneumatic solenoid valves is expected to rise, driving innovation and new product developments in this vital market segment.
Advantages and Limitations of Pneumatic Solenoid Valves
Pneumatic solenoid valves play a crucial role in various automation applications by controlling airflow within a system. One of the significant advantages of these valves is their ability to offer precise control over air pressure and flow rates, which enhances the overall efficiency of pneumatic systems. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for solenoid valves is projected to grow from USD 5.4 billion in 2020 to USD 8.2 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for automated solutions across industries. The quick response time of solenoid valves also minimizes delays in operation, making them ideal for tasks that require immediate action, such as in robotics or assembly lines.
However, pneumatic solenoid valves come with certain limitations. They may be susceptible to wear and tear due to frequent cycling, which can lead to maintenance challenges and increased operational costs over time. Additionally, solenoid valves typically require a continuous power supply, which may not be feasible in all applications, particularly in remote locations. A study by Research and Markets indicates that while the adoption of solenoid valves is on the rise, considerations around energy efficiency and maintenance impact their long-term deployment in some sectors, underscoring the importance of evaluating both benefits and drawbacks in the decision-making process.
Related Posts
-

Your Comprehensive Guide to Sourcing the Best Pneumatic Solenoid Valves for Your Projects
-

Choosing the Right Manufacturer for High Quality Air Solenoid Valve Solutions
-

Top 10 Applications of the Best Pneumatic Solenoid Valves in Industrial Automation
-
How to Choose the Best Solenoid Valves for Your Industrial Applications
-

Tailored Solutions for Enhancing Efficiency with Advanced Solenoid Valves in Industrial Applications
-

Maximizing Efficiency: The Role of Air Flow Control Valves in Modern HVAC Systems and Energy Savings
